While Uploading Certificate Chain Getting the Error Index: -1
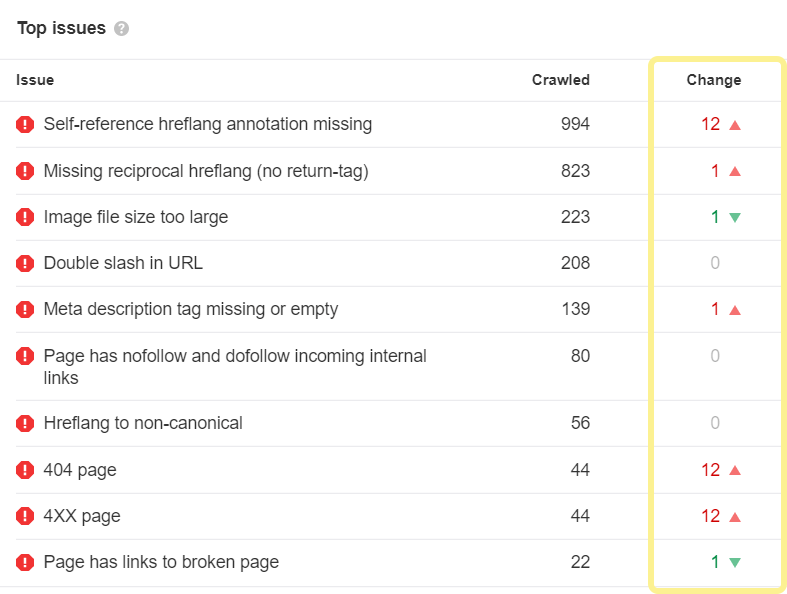
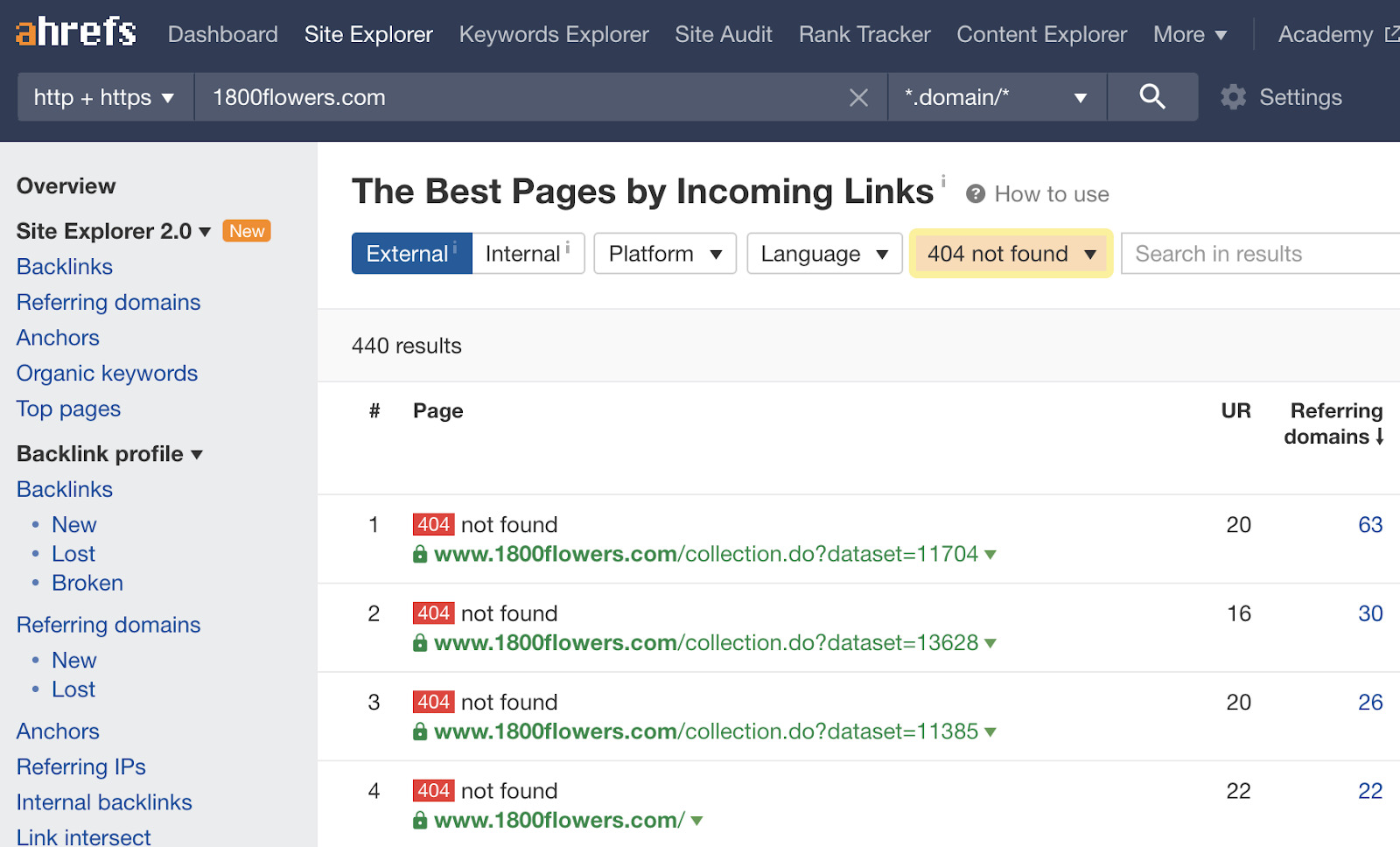
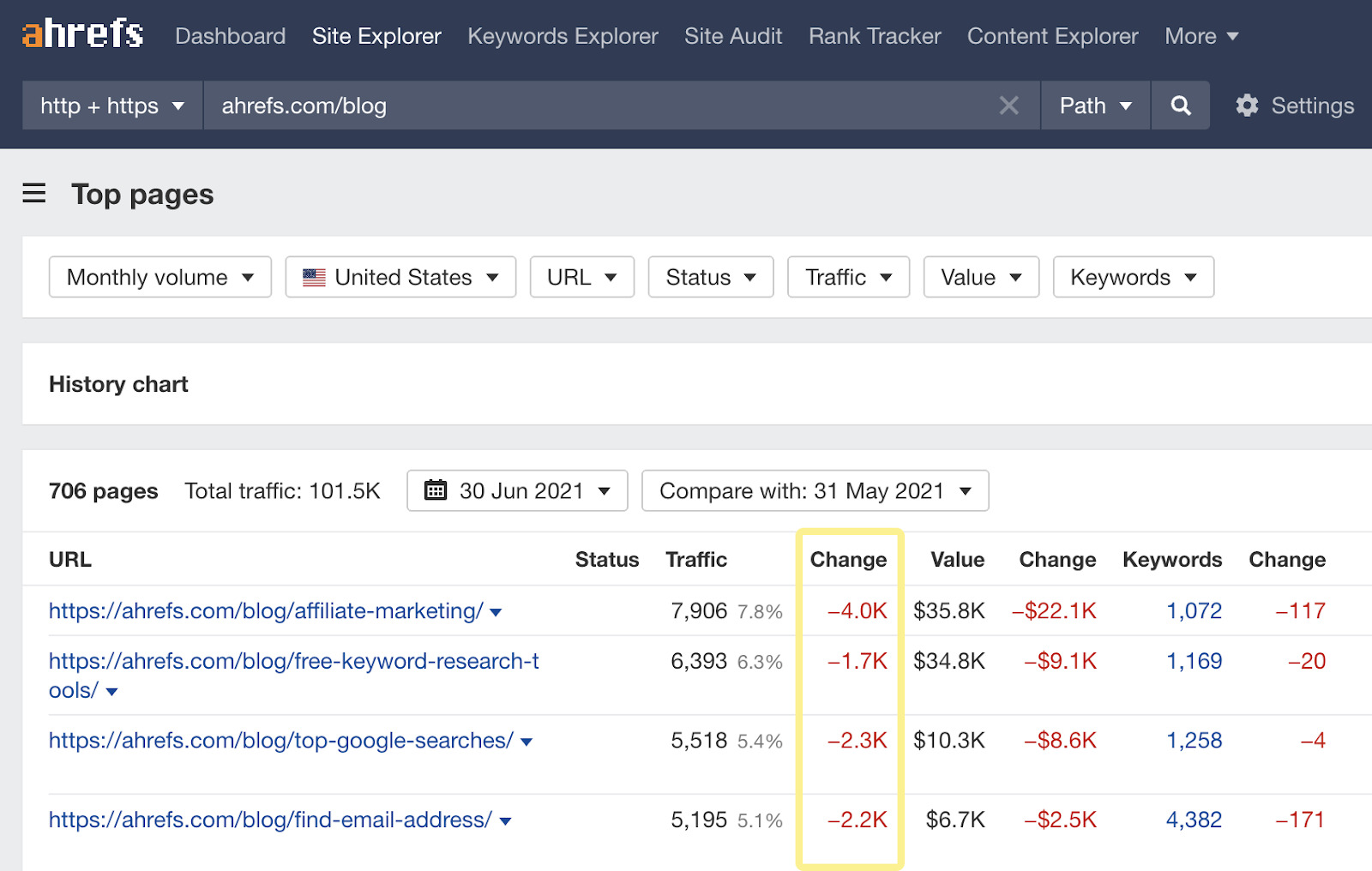
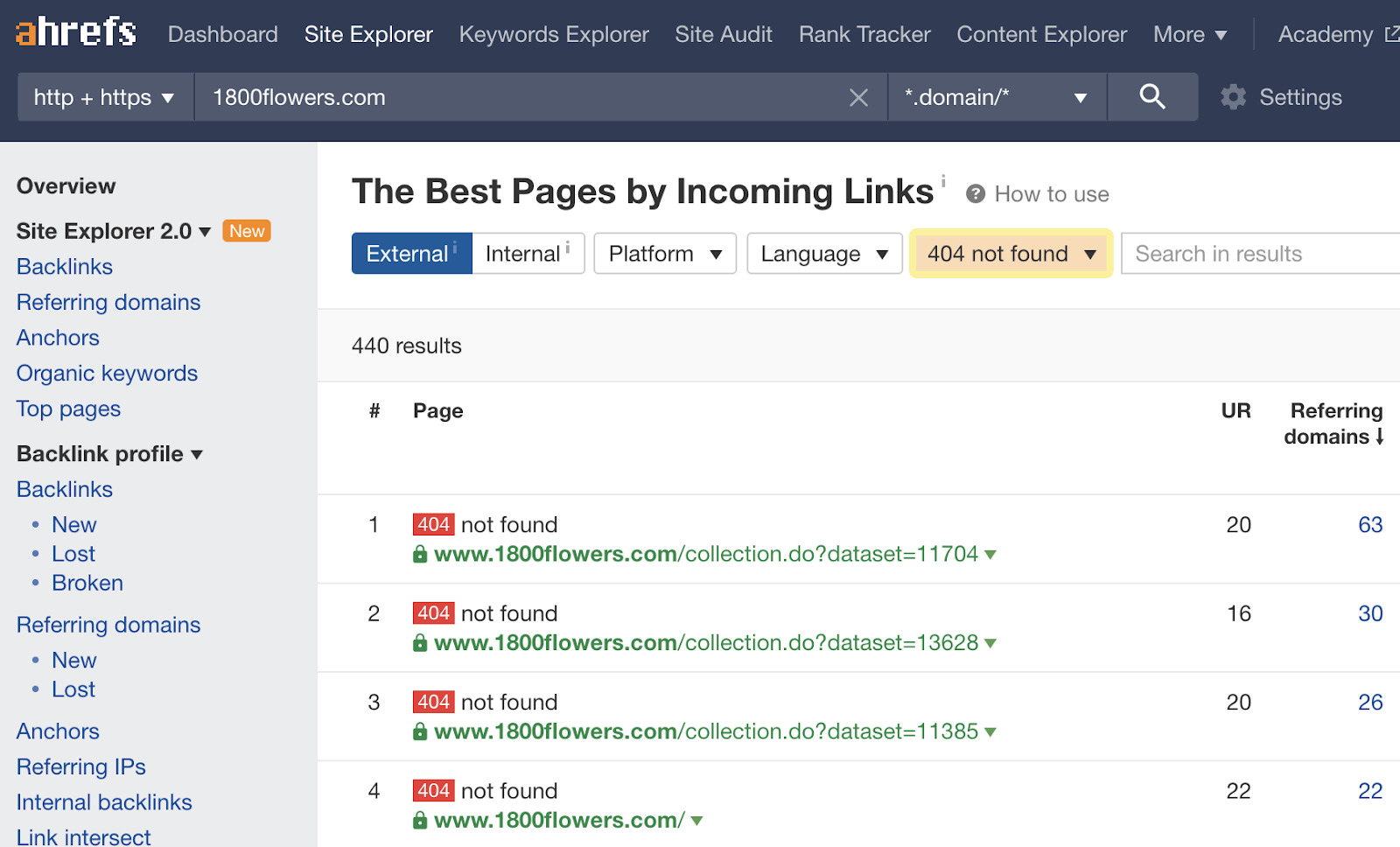
A website migration is a term used to describe whatever significant changes to a website's setup which may impact SEO, such as changes to the domain, URLs, hosting, platform, or pattern. There are many dissimilar kinds of migrations, only the basic steps for planning and troubleshooting are similar. Migrations can be highly complex as they often involve many people and moving parts. Don't panic if everything doesn't get every bit planned; you lot can fix well-nigh annihilation that goes incorrect. In this guide, we'll cover: You lot need to know what is irresolute and who needs to be involved for it to happen. In other words, yous need a plan and a place to track all the moving parts. Y'all'll demand to know all of the people involved, their function, deadlines, and have a process in identify to track everything. A project manager and project direction system helps with this. Trying to exercise it all in email and Slack can go out of command fast. You also desire to have a rollback program, just in case something goes horribly wrong. You should always have a mode to go back to the original state, even if you lot only programme to use it in extreme situations. You'll desire to know the impact of a move, so make sure y'all accept access to GSC and Analytics on the old and new sites (brand a combined view if needed to see both). Some changes may take a few weeks or even months where you may encounter flux, but others may not run across whatsoever changes at all. For instance, if yous're migrating a mid-size site to a new domain, I'd look a few weeks of flux. But if you're combining into an existing site, you may not come across whatever traffic disruptions at all. You also want to do a bit of prep work. I suggest a few steps: Precisely what's involved in a website migration depends on whether the URLs will remain the aforementioned or not. Below nosotros'll discuss both scenarios. This is typically a more straightforward motility—at to the lowest degree SEO-wise—since fewer things are changing. Information technology still may be a complex move, merely many of the tasks involved with these moves are typically more the work of infrastructure/DevOps or developers and not SEOs. These migrations may include: If you are using a staging or dev site, it's best to become access to check for issues before you launch it live. For this, yous're substantially looking for any changes, including things similar: Use the comparison function of Site Audit to encounter changes since your final crawl: There are a couple more issues that may create more than significant bug. These migrations volition usually exist more than complex. The exception is moving from HTTP to HTTPS—which is pretty easy these days. These migrations may include: I wouldn't worry most things similar a redirect chain on the root path or updating links to the site. Fixing the concatenation and updating links won't provide any benefits since signals consolidate because of the redirects. Here'south a quick tip for Site Inspect users: if you alter the scope of your clamber in the project settings to a different domain, your new crawl will be on the new domain and you'll be able to compare it to the clamber on the old domain. You desire to catch changes as early as possible so if you take a dev or staging site, you should crawl this to make sure everything'south okay before pushing changes to a live site. Remember that if an onetime site was using HTTPS and the certificate expires, bots are passed but users will receive an error message and won't exist redirected. There are multi-domain certificates that embrace multiple sites that can help prevent this result. If you see a drop, it's likely related to redirects, something not being able to be crawled, something noindexed, changes to the content or removing content, changes to internal links, or something that changed related to technical SEO. Sidenote. If you're thinking about updating links to your site, y'all may want to update links from pages you control, but I wouldn't carp doing outreach to update links on other sites that point to you. They should consolidate properly with the 301 redirects. It'south non worth the effort to get them changed. In that location are diverse ways to scout the progress of the migration and make certain everything is progressing as it should. There are several various means to look for changes. Every bit I mentioned earlier, y'all tin can change the scope of your clamber in Site Audit and go a comparison that shows yous what inverse. You'll want to wait out for changes to things like: Remember how we created that list of top pages earlier? These are your priority pages. It's worth crawling that list in Site Audit to ensure things like redirects are in place and at that place oasis't been any significant changes. If you prepare a separate project for that listing ahead of fourth dimension, you lot tin can even do a comparison crawl to see changes on these pages quickly. Yous can become folio traffic, keyword traffic and modify history with the Summit Pages and Organic Keywords reports in Site Explorer 2.0. It'due south easy to make comparisons for the aforementioned domain, but if you changed domains, you might desire to consign this data to Excel or Google Sheets to brand a combined view for different periods and meet where any losses may take happened. You lot tin can as well use our crawler to brand sure your redirects are working properly, and links are redirected properly. Here'due south the easiest way to do that: This will prove you lot pages with links to them that we encounter as 404 with our crawler. You might desire to redirect these. Google Search Console has a lot of information to help you with migration. For example, you can check for canonicalization bug using the URL Inspection tool. But enter the URL, and Google volition tell you what canonical they chose. Beyond that, you can export GSC data and make a combined view of your traffic in Excel or Google Information Studio to lookout the migration better. You may too want to utilise a combined view of the folio or keyword data to troubleshoot any losses. The Index Coverage study helps you see how your pages are indexed. If you've uploaded both the old and new sitemap files, you can watch the change in indexing and check for whatsoever issues hither. Past having the sitemap files, yous can get specific coverage reports merely for the pages in those sitemaps. If you lot want to run into an overview of Google crawl activity and any identified issues, the best identify to look is the Crawl Stats report in Google Search Console. There are various reports here to assistance you lot identify changes in crawling behavior, issues with crawling, and give you lot more data well-nigh how Google is crawling your site. You definitely want to look into whatsoever flagged crawl statuses like the ones shown hither: There are also timestamps of when pages were last crawled. If you didn't get a baseline crawl of the site and need to check for differences betwixt the old and the new, bank check archive.org to run into if they have a copy of any of the pages. They besides usually accept copies of robots.txt files from sites that can be useful to see if something went wrong and was accidentally blocked during the procedure. If you don't have access to Google Search Console for a site, you lot tin still cheque canonicalization by pasting a URL in Google. Usually the first page shown volition be the canonical. And once more, if you don't take access to GSC, many other problems related to itch tin can be checked in your log files. Just a warning that the site: search operator sometimes confuses people. If y'all use site:, you're request what Google knows about a specific website. Simply because you see pages there doesn't mean that's how they're indexed or that there's a problem with the migration. I've seen this pb to people doing things like blocking the old site to keep the pages out of the index—which causes bug. Some bug may show up long after migration is over. Migrating websites is no easy feat, and so it's time to gloat if everything went well. Withal, every bit this probably won't exist the final time you exercise a site migration, I'd propose getting together with those involved one more time to go over what went well, what went wrong, what you would change if you had to do it again. Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.
When URLs are the same…
What to expect for
When URLs are different…
Specific to HTTP > HTTPS
Specific to domain changes
All
With Ahrefs
With GSC
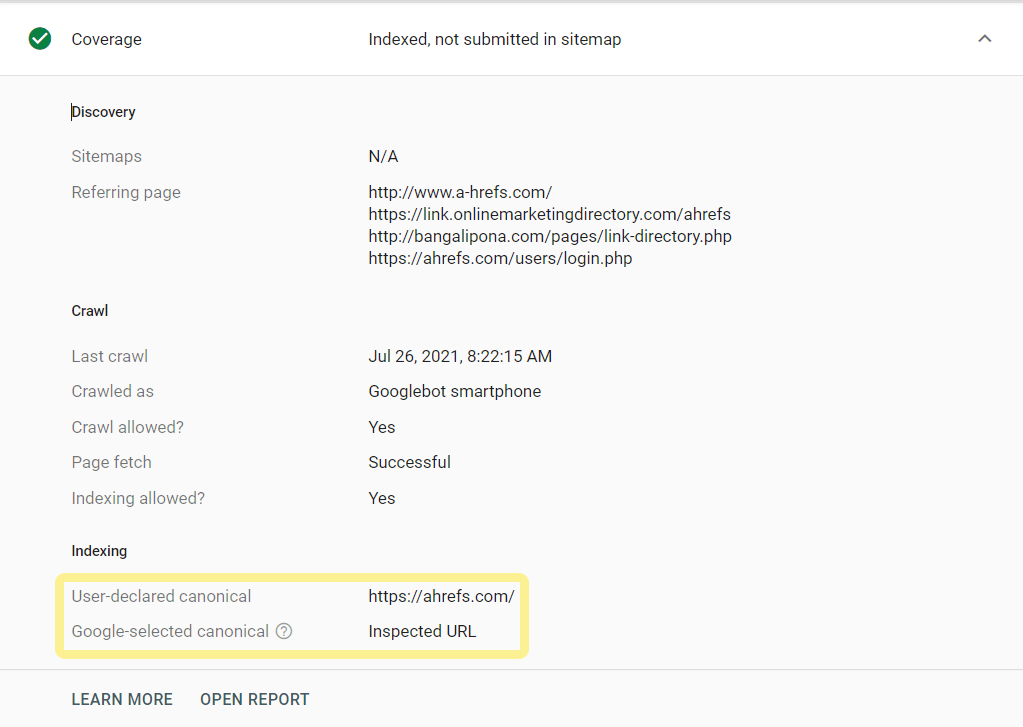
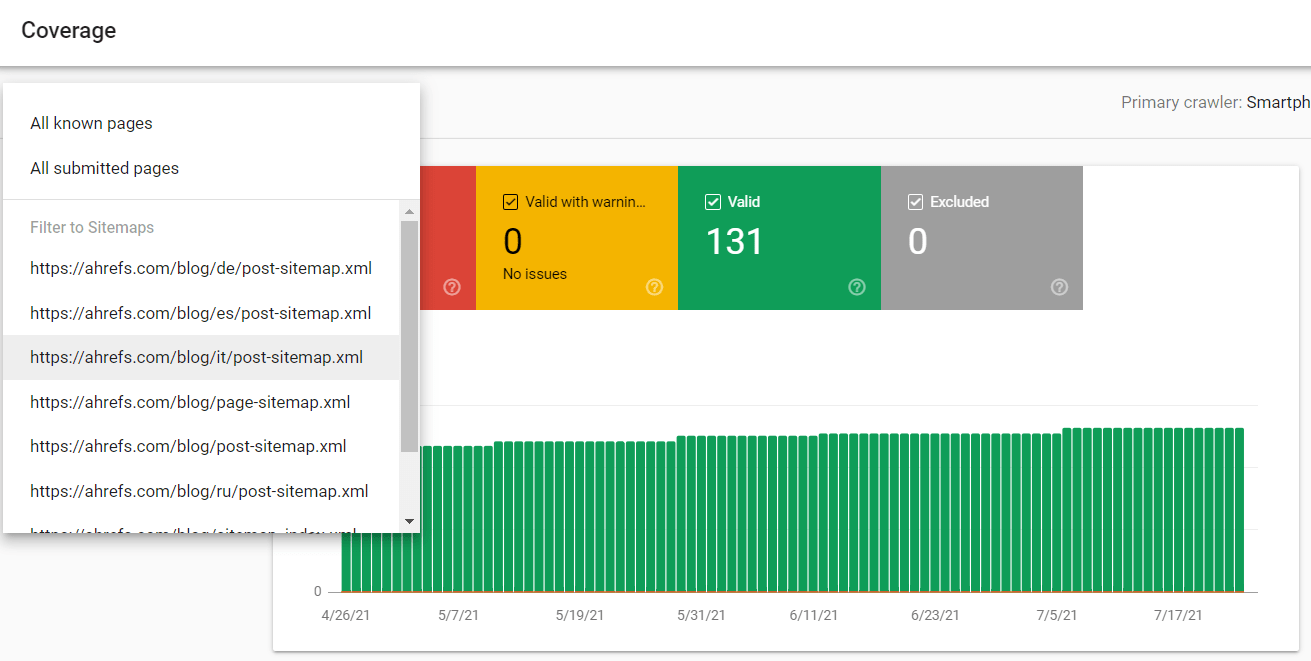

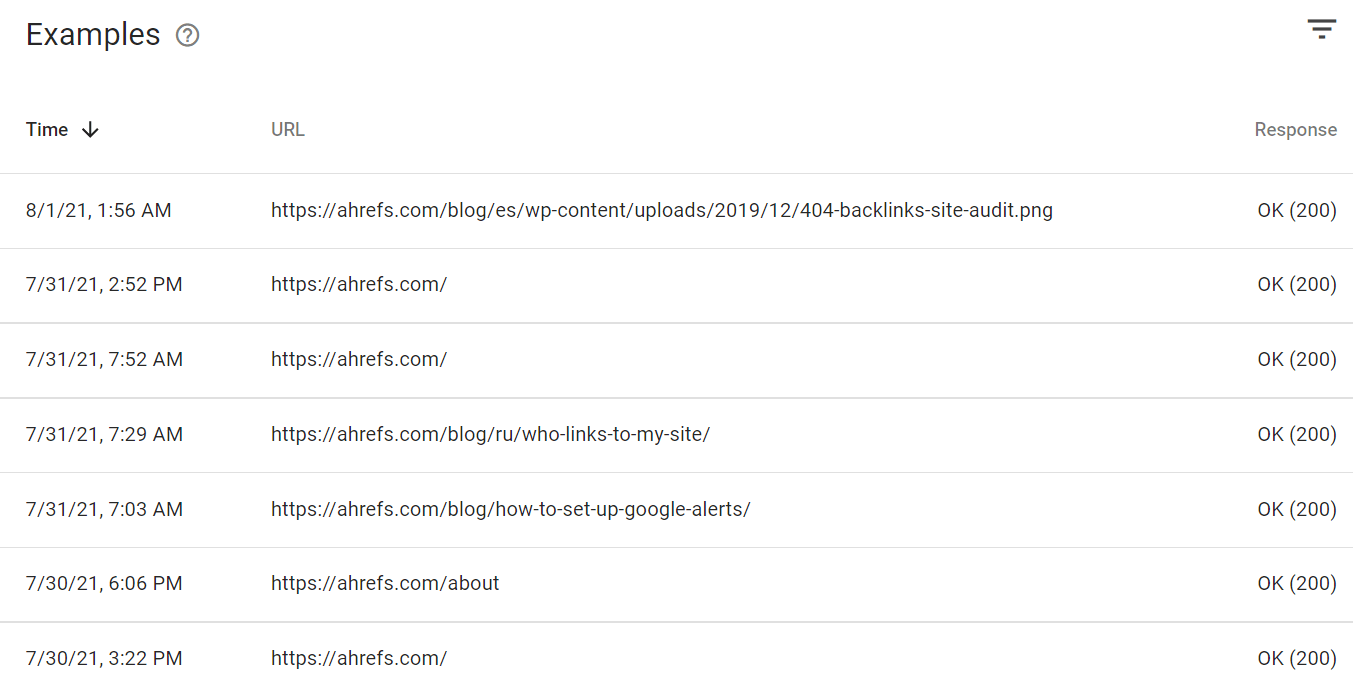
Misc
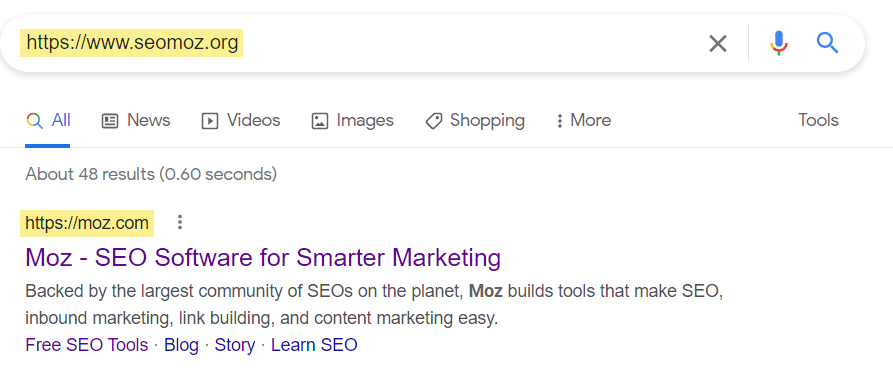
Continue monitoring
Final thoughts
Source: https://ahrefs.com/blog/website-migration/
0 Response to "While Uploading Certificate Chain Getting the Error Index: -1"
Post a Comment